- 1Helmholtz Zentrum München – German Research Center for Environmental Health (GmbH), Research Unit Microbe–Plant Interactions, Neuherberg, Germany
- 2College of Plant Protection, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China
- 3Key Laboratory of Monitoring and Management of Crop Disease and Pest Insects, Ministry of Agriculture, Nanjing, China
- 4ABiTEP GmbH, Berlin, Germany
- 5Fachgebiet Phytomedizin, Institut für Agrar- und Gartenbauwissenschaften, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum FZB42 is a Gram-positive model bacterium for unraveling plant–microbe interactions in Bacilli. In addition, FZB42 is used commercially as biofertilizer and biocontrol agent in agriculture. Genome analysis of FZB42 revealed that nearly 10% of the FZB42 genome is devoted to synthesizing antimicrobial metabolites and their corresponding immunity genes. However, recent investigations in planta demonstrated that – except surfactin – the amount of such compounds found in vicinity of plant roots is relatively low, making doubtful a direct function in suppressing competing microflora including plant pathogens. These metabolites have been also suspected to induce changes within the rhizosphere microbial community, which might affect environment and plant health. However, sequence analysis of rhizosphere samples revealed only marginal changes in the root microbiome, suggesting that secondary metabolites are not the key factor in protecting plants from pathogenic microorganisms. On the other hand, adding FZB42 to plants compensate, at least in part, changes in the community structure caused by the pathogen, indicating an interesting mechanism of plant protection by beneficial Bacilli. Sub-lethal concentrations of cyclic lipopeptides and volatiles produced by plant-associated Bacilli trigger pathways of induced systemic resistance (ISR), which protect plants against attacks of pathogenic microbes, viruses, and nematodes. Stimulation of ISR by bacterial metabolites is likely the main mechanism responsible for biocontrol action of FZB42.
Introduction
Plant rhizosphere is a highly competitive environment in which micro-organisms are abundantly present due to the availability of nutrients actively secreted by the plant root and mucilage. Some of these bacteria which are living within or in the vicinity of plant roots and supporting plant growth are generally referred as being plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR; Kloepper et al., 1980). In many cases their plant growth promoting activity is linked with their ability to suppress soil-borne plant pathogens (bacteria and microfungi), occurring in the competing microflora. Different mechanisms are discussed in this context. Besides production of antimicrobial (“antibiotics”), antiviral and nematicidal compounds, also stimulation of plant induced systemic resistance (ISR; Doornbos et al., 2012), and a beneficial effect on the composition of the host-plant microbiome might contribute to their suppressive effect (Erlacher et al., 2014).
The aim of the present review is to describe the “state of the art” in elucidating interactions within the tripartite system consisting of beneficial bacterium, the pathogen and the plant by using Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 as a model. The aerobic-endospore-forming rhizobacteria belonging to B. amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum (Borriss et al., 2011) are known for enhancing yield of crop plants and for their biocontrol function directed against plant pathogens. The type strain of the subspecies, FZB42T, is commercially used as biocontrol bacterium being especially efficient against fungal and bacterial pathogens (Borriss, 2011). Its plant colonizing ability was demonstrated with a GFP-labeled FZB42 derivative on Lemna minor, Arabidopsis thaliana, maize, tomato, and lettuce using confocal laser scanning microscopy (Fan et al., 2011, 2012). Beneficial effects on plant growth and disease suppression were documented for B. amyloliquefaciens FZB42 on tomato, cucumber, cotton, tobacco, and lettuce for example (Grosch et al., 1999; Yao et al., 2006; Guel et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2009; Chowdhury et al., 2013, 2015).
A comparison of the genomic sequence of FZB42 with that of the non-plant-associated B. amyloliquefaciens type strain DSM7T revealed significant differences in the genomic sequences of both strains (Rueckert et al., 2011). The strains have in common 3345 CDS residing in their core genomes; whilst 547 and 344 CDS were found to be unique in FZB42T and DSM7T, respectively. Notably, ability to synthesize non-ribosomally the antibacterial polyketides macrolactin and difficidin is an unique feature of the subspecies plantarum, whilst capability to synthesize an iturin-like antifungal lipopeptide (LP) is shared with subsp. amyloliquefaciens but not with the other members of the B. subtilis species complex (Figure 1).
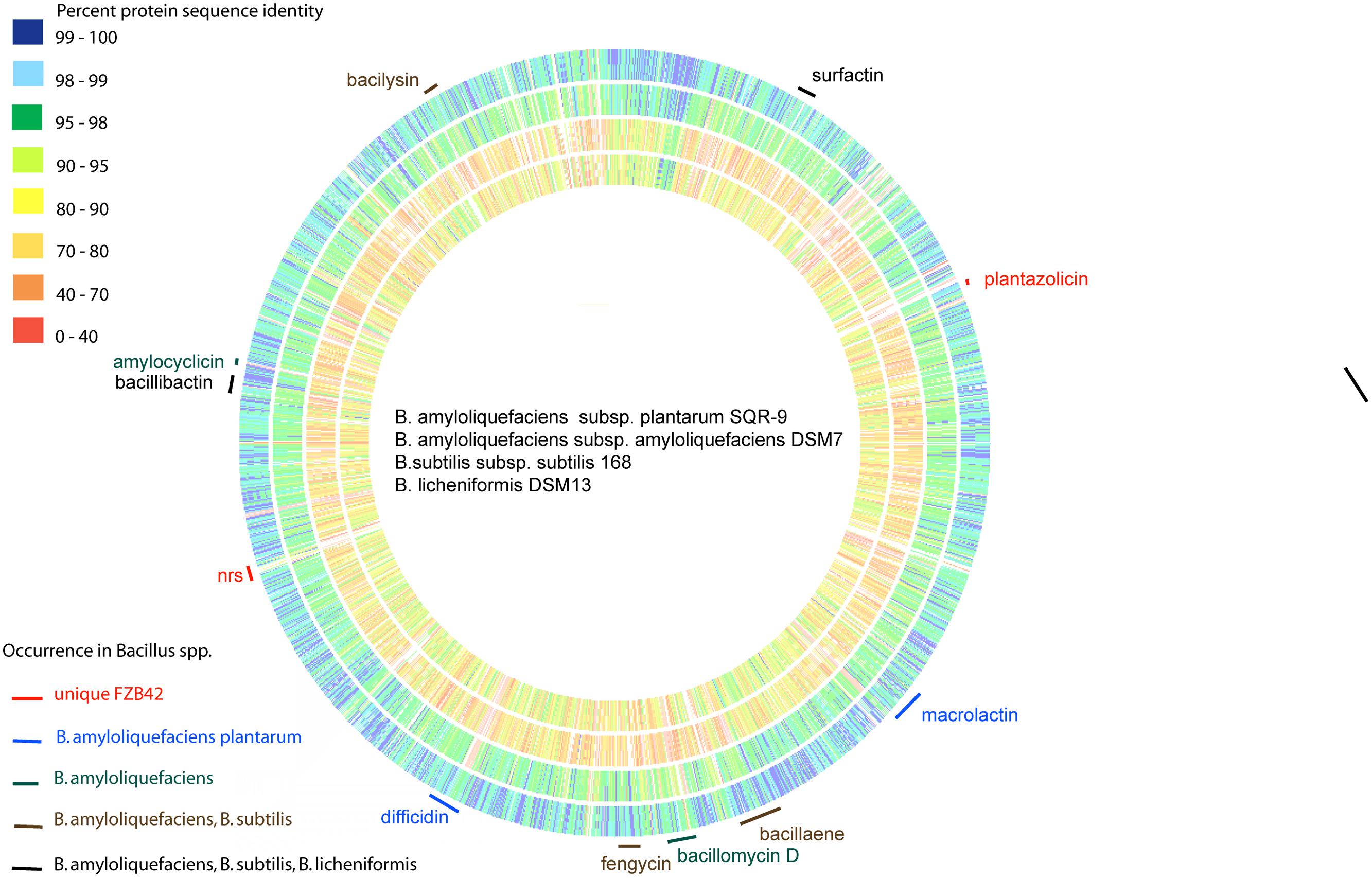
FIGURE 1. Genome comparison of the type strains of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, B. subtilis, and B. licheniformis. The whole genomes of B. amyloliquefaciens plantarum SQR-9 (outside circle), B. amyloliquefaciens amyloliquefaciens DSM7T (second circle), B. subtilis subtilis 168T (third circle), and B. licheniformis DSM13T (inner circle) were aligned with FZB42T using the RAST server (Aziz et al., 2008). The color code indicates % similarity of single gene products. The gene clusters responsible for non-ribosomal synthesis of the polyketides macrolactin and difficidin are unique in B. amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum. The iturin gene cluster (bacillomycin D) occurs also in B. amyloliquefaciens subsp. amyloliquefaciens.
In addition to FZB42T, the genomes of other B. amyloliquefaciens plantarum strains have become recently available (Borriss, 2013). The core-genome formed by 15 B. amyloliquefaciens plantarum genomes contains 3,151 genes, the pan-genome more than 6,000 genes, suggesting a high degree of flexibility in the genomes of such plant-associated B. amyloliquefaciens strains. Fifty-four genes were identified as being unique for subspecies plantarum and did not occur in the free-living soil bacterium B. amyloliquefaciens subsp. amyloliquefaciens, for e.g., gene clusters involved in synthesis of polyketides, and in carbon metabolism (Qiao et al., 2014).
Secondary Metabolites with Biocontrol Function
Analysis of the whole FZB42 genome revealed an impressive capability to produce a diverse spectrum of different secondary metabolites aimed to suppress harmful microbes and nematodes living within the plant rhizosphere (Chen et al., 2007). In total, 11 gene clusters (Table 1) representing more than 9% of the genome are devoted to synthesizing antimicrobial metabolites (Chen et al., 2009a; Borriss, 2013). By contrast, the genomes of the closely related non-plant associated members of the B. subtilis species complex devote only around 5% of their capacity in synthesis of antimicrobials.
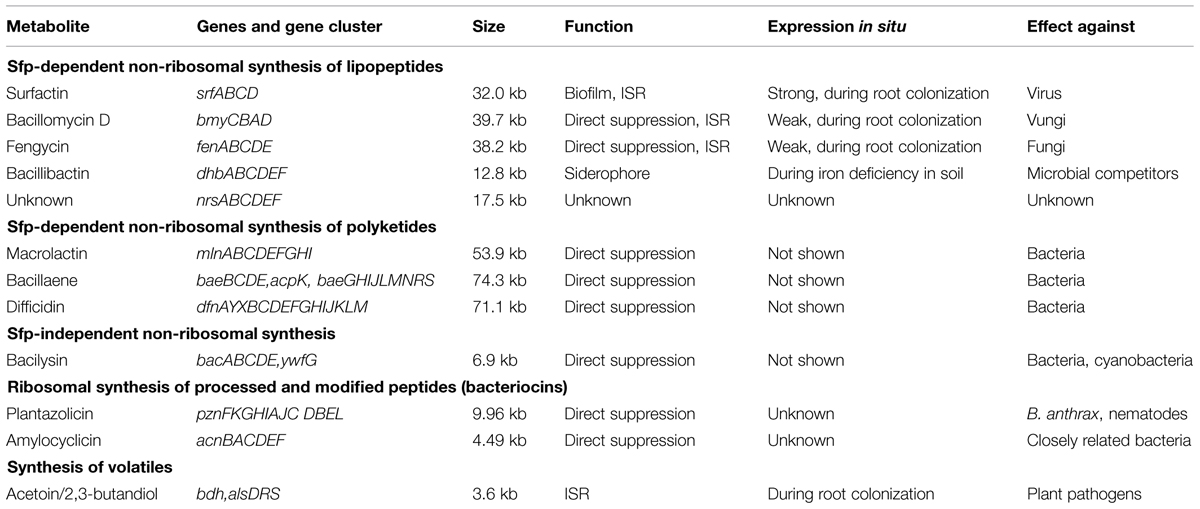
TABLE 1. Genes and gene cluster encoding for biocontrol metabolites in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens plantarum FZB42.
According to numerous in vitro studies it is widely assumed that its antifungal activity is due to non-ribosomal synthesis of the cyclic LP bacillomycin D and fengycin (Koumoutsi et al., 2004), whilst its antibacterial activity is mainly due to non-ribosomally synthesized polyketides (Chen et al., 2006), and bacilysin (Chen et al., 2009b), and ribosomally synthesized bacteriocins (Scholz et al., 2011, 2014).
Lipopeptides Direct Antifungal Activity
Lipopeptides are non-ribosomally synthesized by peptide synthetases (NRPS). NRPS are giant enzymes composed of modules that house repeated sets of functional domains, which select, activate, and couple amino acids drawn from a pool of nearly 500 potential building blocks (Walsh et al., 2013). Five gene cluster involved in non-ribosomal synthesis of cyclic LP and the iron-siderophore bacillibactin were identified in the genome of FZB42 (Table 1). Three of the respective gene clusters were assigned for synthesis of surfactin, fengycin, and bacillomycin D. Bacillomycin D was identified as being the most powerful antifungal metabolite in vitro produced by FZB42 (Figure 2). The heptapeptide moiety of bacillomycin D, belonging to the iturin family of cyclic LP, is attached to a β-amino fatty acid chain of variable length (C14–C17). The peptide moiety of the heptapeptide surfactin is linked to a β-hydroxyl fatty acid (C12–C16), whilst the fengycin decapeptides are linked to a β–hydroxyl fatty acid chain (C 14–C18). Their synthesis is accomplished by multimodular peptide synthetases and depends on a functional phospho-pantheinyl transferase (Sfp) which transfers 4′- phosphopantetheine from coenzyme A to the carrier proteins during non-ribosomal synthesis.
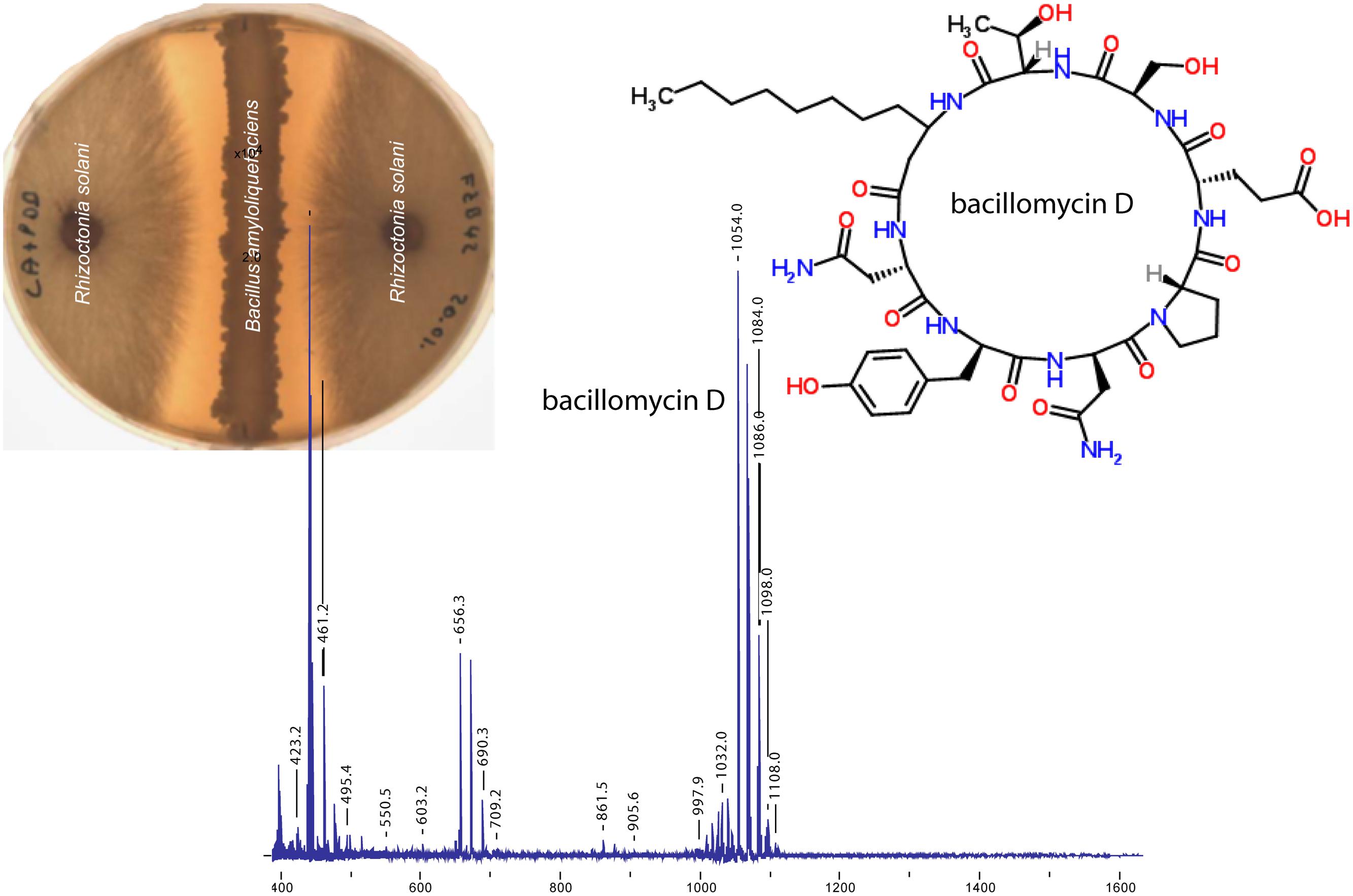
FIGURE 2. Effect of FZB42 on Rhizoctonia solani. A clear inhibition zone indicating growth suppression of the fungal pathogen is visible on agar plates simultaneously inoculated with both microbes. Bacillomycin D was detected as the only prominent compound by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization coupled to time of flight (MALDI TOF) mass spectrometry of samples taken from the surface of the agar plate within the inhibition zone (compiled from data obtained by J. Vater, TUB and K. Dietel, ABiTEP GmbH).
For a long time the plant protective activity of PGPR has been correlated with the potential to secrete a wide array of antibiotic compounds upon growth as planktonic cells in isolated cultures under laboratory conditions (Velivelli et al., 2014). A recent comparative study performed with six strains belonging to the B. subtilis/amyloliquefaciens species complex corroborated our earlier finding that antifungal activity is linked with the ability to produce cyclic LP. Remarkably, production of iturin and fengycin in B. amyloliquefaciens was enhanced in presence of certain phytopathogens (Cawoy et al., 2015). This is in line with a recent finding that non-ribosomal synthesis of antifungal and antibacterial compounds including bacillibactin is stimulated in presence of plant pathogens under laboratory conditions (Li et al., 2014).
We determined expression of the corresponding secondary metabolites by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization coupled to time of flight (MALDI TOF) mass spectrometry from FZB42 cultures grown in liquid Landy medium under laboratory conditions. Except the orphan nrs gene cluster, all expected bioactive compounds were synthesized in reasonable amounts. However, the iron siderophore bacillibactin was detected only under iron-deprived conditions. In recent years, it has become doubtful, that synthesis of metabolites by the planktonic cells grown under laboratory conditions does correspond to their capability to produce those compounds under true environmental conditions, e.g., when grown in biofilm-related structures on the surface of plant tissues.
During last years, Ongena et al. (2007) performed pioneering work in elucidating antibiotic production in planta using MALDI Mass Spectrometry Imaging (MSI). They investigated antibiotic production in a gnotobiotic system in which the plantlet and the associated B. amyloliquefaciens S499, a close relative of FZB42, were growing on a gelified medium covering the MALDI target plate. Under these conditions S499 grows as biofilm on the surface of the plant roots, allowing exact assays of secondary metabolites in the vicinity of root surface. Surfactins were detected in the root environment in much higher relative amounts, which are representing more than 90% of the whole LP production, and their synthesis is rapidly progressing during early biofilm formation. Syntheses of iturin and fengycin were also detected, but found delayed until the end of the aggressive phase of colonization (Nihorimbere et al., 2012; Debois et al., 2014). Earlier experiments performed with FZB42 colonizing duckweed (Lemna minor) plantlets corroborated that surfactin is the most prominent compound which could be detected by MALDI TOF MS in the plant–bacteria system (Idris et al., 2007). Recently, we examined the in situ production of selected secondary metabolites by FZB42 in the lettuce rhizosphere using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled to time of flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-qToF-MS). The LP surfactin, fengycin and bacillomycin D were identified in the rhizosphere of lettuce plants grown in an axenic system and bacterized with FZB42 for 7 days. Interestingly, the presence of the phytopathogen Rhizoctonia solani in the axenic system increased the production of surfactin and bacillomycin D by FZB42 (Chowdhury et al., 2015). The increase in the production of bacillomycin D in the presence of R. solani pointed to an antibiosis effect and the recognition and response of FZB42 to the fungal stimulus. This was in accordance with the recent investigation with different strains of B. amyloliquefaciens including FZB42 showing enhanced production of iturins and fengycins in response to signals emitted by phytopathogens like Fusarium oxysporum and Botrytis cinerea (Cawoy et al., 2015).
An early surfactin secretion could be of biological relevance since this LP, although less fungitoxic than iturins and fengycins, is essential for moving on tissues (Kinsinger et al., 2003) and for matrix formation in biofilms (Hofemeister et al., 2004; Lopez et al., 2009a,b). Considering the relative low amounts of the fungitoxic iturins and fengycins in vicinity of plant roots, it can be concluded that their biocontrol effect is possibly less important. The same is true for the iron siderophore bacillibactin, which was not detected, possibly due to a relative high level of accessible iron ions under the conditions of the artificial plant–bacteria associations applied in these studies.
Non-Ribosomal Polyketides and Bacilysin Direct Antibacterial Activity In Vitro
The polyketides, non-ribosomally synthesized by FZB42 (Chen et al., 2006; Schneider et al., 2007), have been extensively reviewed previously (Chen et al., 2009a,c; Borriss, 2013). The three gene clusters encoding the modularly organized polyketide synthases (PKS) for the synthesis of bacillaene, macrolactin, and difficidin cover nearly 200 kb, and are the largest ones, which are occurring in the FZB42 genome (Table 1). Difficidin is the most effective antibacterial compound produced by FZB42T, but also macrolactin and bacillaene possess antibacterial activity. Difficidin is efficient in suppressing plant pathogenic bacterium Erwinia amylovora, which causes fire blight disease in orchard trees (Chen et al., 2009b).
Another product of non-ribosomal synthesis, the dipeptide bacilysin consisting of anticapsin and alanine moieties, was found as also being involved in suppression of E. amylovora. By contrast to the LP and polyketides mentioned above, bacilysin synthesis is not dependent on the Sfp PP-transferase. A mutant strain CH3, with a disruption of the sfp gene and unable to produce any polyketide or LP, was still able to synthesize bacilysin and to suppress E. amylovora (Chen et al., 2009b). Recent experiments, performed by the group of XueWen Gao, Nanjing Agriculture University, demonstrated that bacilysin, is efficient in suppressing Microcystis aeruginosa, the main causative agent of cyanobacterial bloom in lakes and rivers (Wu et al., 2014). However, corroborating these results in field trials has to be done. It is interesting to note that non-ribosomal LP such as the plant immunity elicitor surfactin or the highly fungitoxic iturins and fengycins were readily produced albeit in different time frames and quantities in the vicinity of plant roots, whilst polyketides, bacilysin, and other bioactive compounds have not been detected till now in plants colonized by B. amyloliquefaciens (Debois et al., 2014).
In light of these findings the question arises what is the physiological function of bacillaene and other polyketides, when these compounds are apparently not involved in inhibition of competitors in natural habitat? It has been suggested that sublethal concentrations of antibiotics may have a role as signaling molecule, e.g., in modulating transcription (Fajardo and Martinez, 2008). Interestingly, the polyketide bacillaene, produced in B. subtilis NCIB3610, functions as a significant defense protecting Bacillus cells from predation by Myxococcus xanthus (Müller et al., 2014).
Bacteriocins Suppress Phytopathogenic Bacteria and Nematodes
Antimicrobial peptides, ribosomally synthesized as linear precursor peptides, remained unknown in B. amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum for a long time with one remarkable exception: mersacidin, a B-type lantibiotic, was detected in Bacillus sp. HIL Y85 (Chatterjee et al., 1992). The strain HIL Y85 was later classified as being B. amyloliquefaciens plantarum (Herzner et al., 2011). Nowadays, mersacidin production was also detected in B. amyloliquefaciens B9601-Y2 (He et al., 2012). Genes involved in mersacidin self-protection reside also in the genome of FZB42. Transfer of mersacidin biosynthesis genes from HIL Y85 resulted in efficient mersacidin production by the surrogate strain constructed from the FZB42 host (Herzner et al., 2011).
Another representative of the type B lantibiotics, amylolysin from B. amyloliquefaciens GA1, was recently described. These lantibiotics are active on an array of Gram-positive bacteria, including Listeria sp. and methicillin resistant S. aureus by interacting with the membrane lipid II (Arguelles Arias et al., 2013).
Driving force in our search for ribosomally synthesized peptides in FZB42 was the finding that the FZB42 mutant RS06, which is deficient in the Sfp-dependent synthesis of LP, polyketides, and in the Sfp-independent bacilysin production (Chen et al., 2009b), still produced an antibacterial substance active against B. subtilis HB0042. In fact, a metabolite (cpd1335) with a molecular mass of [M+H]+ = 1336 Da was assigned by MALDI TOF MS in FZB42 and in RS06, as well. The compound was named plantazolicin, PZN, and the respective gene cluster consisting of 12 genes was identified by cassette mutagenesis. Plantazolicin was characterized as a highly modified peptide undergoing several steps of modification after synthesis. It ruled out that it is a thiazole/oxazole-modified microcin (TOMM) resembling microcin B17 and streptolysin S. Plantazolicin displayed antibacterial activity toward closely related Gram-positive bacteria. Due to its extensive degree of modification, Pzn is highly protected from premature degradation by peptidases within the plant rhizosphere (Scholz et al., 2011). Remarkably, the human pathogen B. anthracis was found sensitive against PZN and underwent massive lysis at 4 μg mL-1 (Molohon et al., 2011). The exact structures of plantazolicin A and B, were elucidated, unveiling a hitherto unusual number of thiazoles and oxazoles formed from a linear 14mer precursor peptide (Kalyon et al., 2011).
Parasitic nematodes of plants are important plant pathogens that represent a significant financial burden on agriculture. FZB42 has been shown to reduce nematode eggs in roots, juvenile worms in soil, and plant galls on tomato (Burkett-Cadena et al., 2008). In order to identify specific-nematicide-related genes, a random transposon insertion library of FZB42 was screened for relevant genes involved in nematicidal activity and – surprisingly – a gene within the pzn gene cluster was identified as a pathogenic factor against nematodes. Further experiments revealed that PZN displayed a moderate nematicidal activity (Liu et al., 2013).
By transposon mutagenesis of the FZB42 mutant strain RS06, which is deficient in Sfp-dependent synthesis of LP, polyketides, and bacilysin, we identified a hitherto unknown gene cluster involved in synthesis and posttranslational processing of a novel circular bacteriocin, named amylocyclicin (Figure 3). It became apparent that amylocyclicin inhibits growth of bacterial strains closely related to FZB42 suggesting that this bacteriocin might have a function in competing with other Bacillus strains attracted to the plant rhizosphere (Scholz et al., 2014).
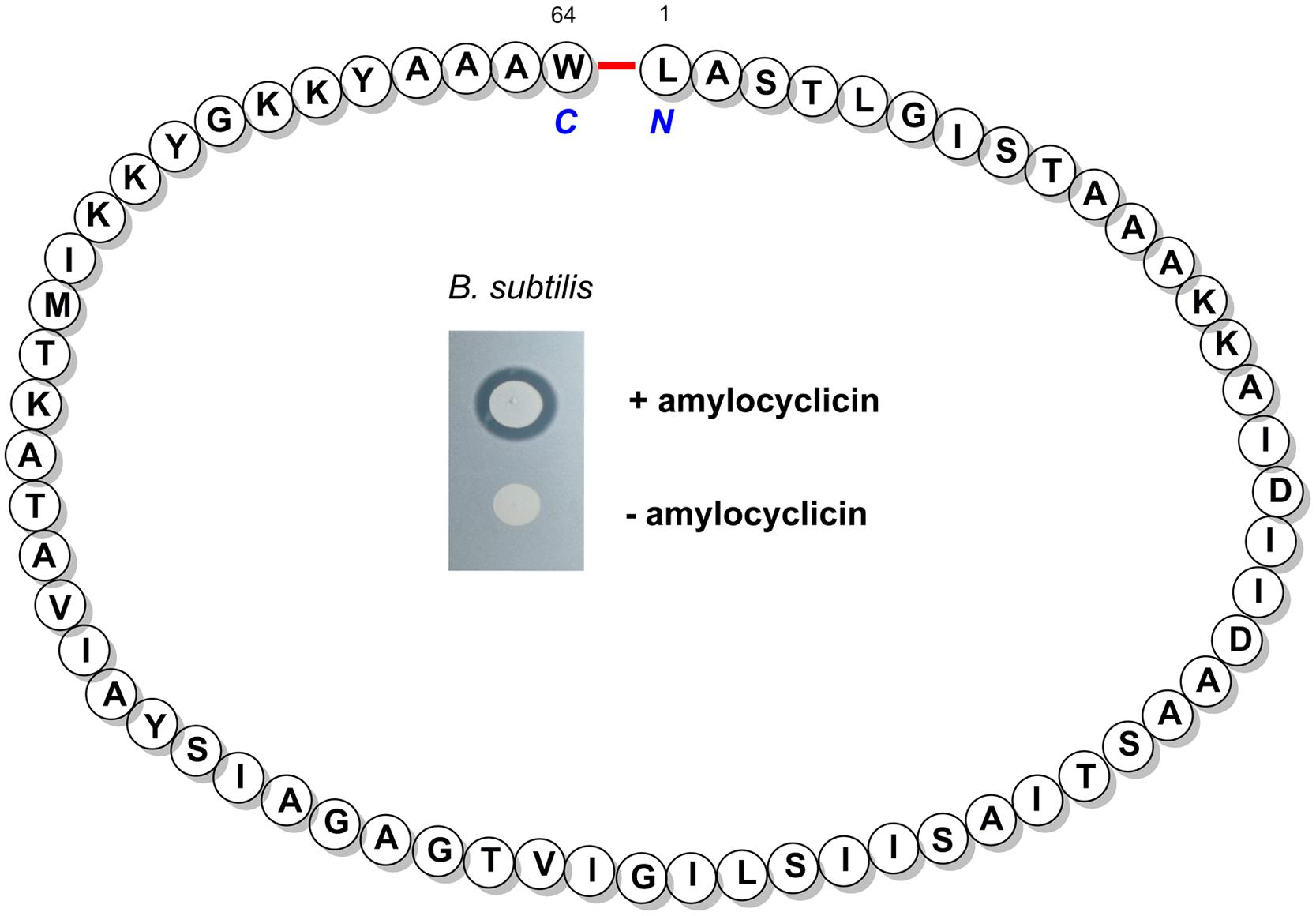
FIGURE 3. The structure of the mature bacteriocin amylocyclicin bearing a head-to-tail cyclization of L1 and W64. Inset: Amylocyclicin effect on a related B. subtilis strain without immunity against the bacteriocin was demonstrated by a spot-on-lawn test performed with a amylocyclicin producing (Top) and non-producing FZB42 strain (Bottom).
Persistence of FZB42 and its Impact on the Root Microbiome
It is commonly accepted, that the structure of the microbial community colonizing plant roots is important for the plant’s well-being and its resistance against pathogens. The root microbiota is strongly affected by soil type, as well as by the genotype of the host plant (Hartmann et al., 2009; Bulgarelli et al., 2012). FZB42 is able to colonize roots of lettuce plants growing in sandy loam soil, but presence of vegetative cells at the root surface becomes slowly reduced around 6 weeks after inoculation suggesting, that FZB42 is not a strong competitor of the indigenous root microflora (Borriss, 2015). However, our results demonstrated that FZB42 is able to reduce the disease severity of bottom rot caused by soil-borne pathogen R. solani on lettuce (Chowdhury et al., 2013).
As revealed by T-RFLP community fingerprinting and taxonomic profiling of metagenome sequences, application of FZB42 on field grown lettuce, independent of its mode of application, did not shift the composition of rhizosphere bacterial community in a measurable extent (Chowdhury et al., 2013; Kröber et al., 2014). Similar results were also found for B. amyloliquefaciens BNM122 in soybean (Correa et al., 2009). By contrast, inoculation with the pathogen did change the rhizosphere microbial community structure. Using the same setup in greenhouse experiments, the effect of FZB42 and the pathogen R. solani on the microbial community of lettuce was more deeply analyzed by 454-amplicon sequencing focusing on the presence of gamma-proteobacteria (Erlacher et al., 2014). Clear differences between plants infected by R. solani compared to non-inoculated healthy plants were found, corroborating the results obtained by T-RFLP. A significant increase in gamma-proteobacterial diversity was detected in samples inoculated with the pathogen, whilst in the presence of FZB42 and the pathogen together this increase was less distinct, suggesting a selective compensation of the impact of a pathogen on the indigenous plant-associated microbiome by FZB42. The method called ‘fragment recruitments’ was used to track the persistence of the FZB42 inoculant. The number of DNA fragments corresponding to FZB42 decreased in the course of the plant cultivation. After 5 weeks, about 55% of the initial number of FZB42 DNA was still traceable within the rhizosphere of lettuce in the field (Kröber et al., 2014).
Plant Defense is Triggered by Plant-Associated Bacilli including FZB42
The biocontrol effect shown by FZB42 could rely on the potential antimicrobial activity of several bioactive secondary metabolites. However, except surfactin, concentration of antifungal LP determined in planta was found relatively low (Nihorimbere et al., 2012; Chowdhury et al., 2015). Moreover, antibacterial polyketides and other bioactive compounds were not detected so far in the vicinity of plant roots colonized by PGPR Bacilli (Debois et al., 2014). Therefore, it is tempting to speculate that ISR triggered by surfactin, microbial volatile organic compounds (mVOCs) and, possibly, other hitherto unidentified secondary metabolites, is a main factor in suppressing plant pathogens by PGPR Bacilli. ISR is defined as ‘enhanced defensive capacity of the entire plant against a broad spectrum of pathogens; acquired upon local induction, e.g., at roots, by beneficial microbes’ (Pieterse et al., 2014). ISR was initially demonstrated in Pseudomonas sp. and other Gram-negative root associated bacteria, but later it was demonstrated that several Bacillus sp. including B. subtilis and B. amyloliquefaciens elicit ISR in Arabidopsis, several vegetables, tobacco, and tropical crops (Kloepper et al., 2004). Typically, the rhizobacteria induce plant defense via jasmonic acid (JA) and/or ethylene (ET) signaling pathways. ISR is distinct from systemic acquired resistance (SAR) in which the response is triggered by pathogenic microorganisms associated with the aerial portions of the plant. In systemic tissues, SAR is characterized by increased levels of the hormone salicylic acid (SA). Interestingly, plants treated with B. pumilus had greatly increased levels of SA, compared to the untreated control (Zhang et al., 2002).
Selected Bacillus PGPR strains emit mVOCs that can elicit plant defenses. Exposure to VOCs consisting of 2,3-butanediol and acetoin (3-hydroxy-2-butanone) from PGPR B. amyloliquefaciens activates ISR in Arabidopsis seedlings (Ryu et al., 2003). Arabidopsis thaliana plants exposed to B. subtilis strain FB17, results in reduced disease severity against Pseudomonas syringae compared to plants without FB17 treatment. Exogenous application of acetoin triggers ISR and protects plants against the pathogen in the aerial parts (Rudrappa et al., 2010). In this context it is worth to mention, that expression of acetolactate synthase, AlsS of FZB42, an enzyme involved in the synthesis of acetoin (Figure 4) was strongly increased in the presence of maize root exudates during late exponential growth phase (Kierul et al., 2015), suggesting that root exudates play a role in eliciting of acetoin biosynthesis in FZB42. In the same study, it was found that two proteins related to chemotaxis and motility, flagellar hook-associated protein II (FliD) and the Hag flagellin protein, were increased in the presence of root exudates. Flagellin proteins bearing the flg22 elicitor signal are recognized by most plant plasma membrane-localized pattern recognition receptors and are thus thought to prime plant basal defense against potential pathogens. B. amyloliquefaciens FZB24 and FZB42 applied to tobacco roots led to a reduction of tobacco mosaic virus symptoms visible on tobacco leaves, and to decreasing amounts of virus proteins present in leaf tissues. Due to the spatial distance between the beneficial bacterium and the pathogen, plant ISR, stimulated by the rhizobacterium, might be responsible for this effect. In fact, it was shown that the application of PGPR Bacilli led to ISR toward viral infection and enhanced plant growth (Wang et al., 2009).
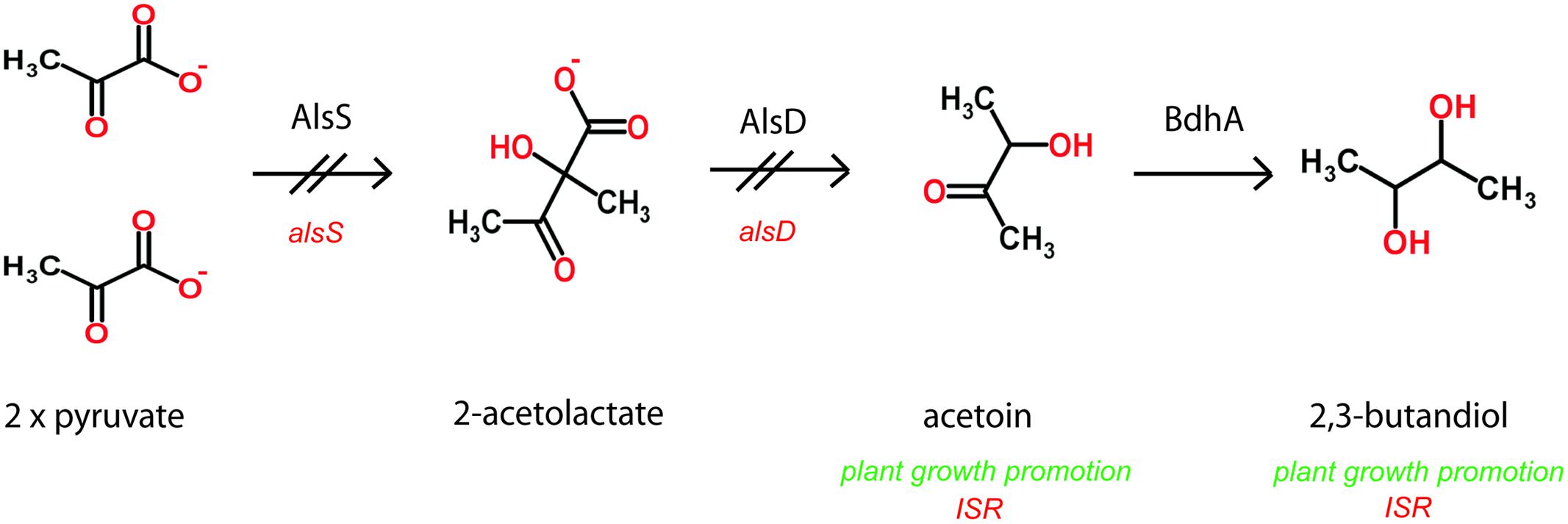
FIGURE 4. Anaerobic and aerobic formation of 2,3-butanediol via acetoin involves acetolactate synthase and decarboxylase encoded by the alsSD operon. The alsS insertion mutation abolishes synthesis of 2,3-butandiol (Renna et al., 1993; Cruz Ramos et al., 2000).
The induction of ISR when treated with Gram-negative PGPRs is mediated primarily through the plant hormones JA, a lipoxygenase pathway product, and ET. By contrast, SA appears to be a critical plant messenger of pathogen exposure and disease resistance in SAR (Pieterse et al., 2014). Notably, a simultaneous activation of ET and SA-signaling pathways by Bacillus sp. was found when defense compromised mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana were exposed to FB17, whilst JA was not essential (Rudrappa et al., 2010).
In order to determine the signaling pathways triggered by FZB42, the expression of several marker genes in lettuce plants, exposed to FZB42 and the pathogenic fungus R. solani, were analyzed by quantitative real time (RT)-PCR (Chowdhury et al., 2015). In absence of the pathogen, FZB42 increased expression of PR1 (pathogenesis protein 1, SA marker gene), and plant defensing factor 1.2 (PDF1.2; defensin, JA/ET marker gene), suggesting that SA and ET pathways are involved in up-regulating defense response in lettuce. In simultaneous presence of FZB42 and the pathogen R. solani, PDF1.2 expression was dramatically enhanced, suggesting a synergistic activation of the JA/ET pathway, whilst the SA pathway – as indicated by a decreased expression of PR-1 – was suppressed in presence of both antagonists. This is in accordance with previous results (Sarosh et al., 2009) suggesting that B. amyloliquefaciens can induce systemic resistance in oilseed rape against Botrytis cinerea through a JA dependent PDF 1.2 expression.
The circular LP surfactin and to a minor extent fengycin can act as elicitors of host plant immunity and contribute to increased resistance toward further pathogenesis development in bean and tomato plants (Raaijmakers et al., 2010). In bean, purified fengycins and surfactins provided a significant ISR-mediated protective effect against the fungal pathogen Botrytis cinerea, similar to the one induced by living cells of the producing strain B. amyloliquefaciens S499 (Ongena et al., 2007). Similarly, low concentrations of surfactin induced several early plant-defense related events in tobacco cells (Jourdan et al., 2009). A strong correlation was found between defense-inducing activity (e.g., stimulation of ROS production) and the amount of surfactin produced by several isolates belonging to the B. subtilis/amyloliquefaciens complex (Cawoy et al., 2014). Combined application of surfactin and live cells of mutant strain FZB42-AK3 (produces surfactin, but not bacillomycin D and fengycin) reduced gray leaf spot disease caused by Magnaporthe oryzae in ryegrass Lolium perenne. A multilayered ISR defense response in ryegrass cells was registered, such as: (1) enhanced accumulation of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), (2) elevated cell wall/apoplastic peroxidase activity, (3) deposition of callose and phenolic/polyphenolic compounds underneath the fungal appressoria in leaves, (4) hypersensitive response (HR)-type reaction together with enhanced expression of peroxidase, oxalate oxidase, phenylalanine ammonia lyase, lipoxygenase, and putative defensins (Rahman et al., 2014).
We found that the dramatic increase of the PDF1.2 gene expression in simultaneous presence of B. amyloliquefaciens and R. solani occurred only when wild type cells of FZB42 were applied. Mutant strains deficient in non-ribosomal synthesis of LP and polyketides did not stimulate expression of the JA/ET pathway, suggesting that cyclic LP contribute to the ISR plant response triggered by FZB42 (Chowdhury et al., 2015).
Conclusion
Biocontrol of plant pathogens is an important feature of Bacillus inoculants applied for a more sustainable agriculture. FZB42, when added to plants, does not affect the root microbiome, but FZB42 seems to restore, at least in part, the original community structure which has been previously altered by competing plant pathogens, such as fungus R. solani.
Recent results mainly obtained with B. amyloliquefaciens FZB42 and other representatives of the B. amyloliquefaciens plantarum subspecies support the hypothesis that stimulation of plant ISR by bacterial metabolites, such as surfactin and volatiles, is the key mechanism in the biocontrol action of Gram-positive endospore-forming bacteria. By contrast, a direct effect of the numerous antimicrobial secondary metabolites in suppressing pathogens occurring in the plant rhizosphere seems to be of minor importance. In addition, sublethal concentration of other LP, such as fengycin and iturins, might prime plant defense response against plant pathogens. The role of non-ribosomal polyketides and of an emerging number of small peptide molecules (bacteriocins) ribosomally synthesized by FZB42 and other PGPR Bacilli in suppressing concomitant phytopathogens occurring in plant rhizosphere remains elusive. Figure 5 summarizes the main points of our present knowledge about the effect of plant-associated Bacillus within the tripartite system consisting of beneficial Gram-positive bacterium, pathogen and plant.
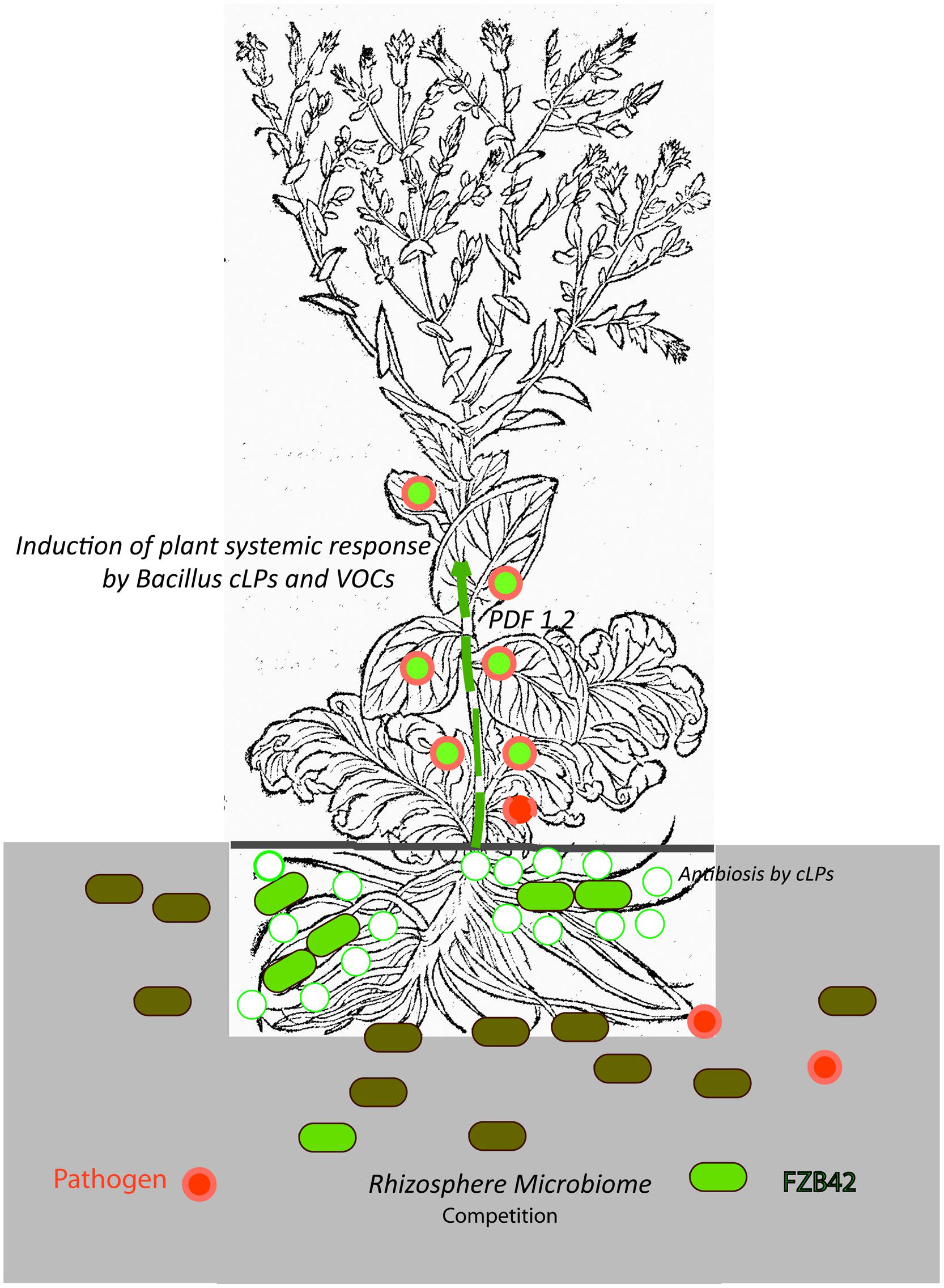
FIGURE 5. Biological control exerted by the plant-beneficial bacterium FZB42. The cartoon illustrates our present picture about the complex interactions between a beneficial Gram-positive bacterium (FZB42, light green), a plant pathogen (R. solani, symbolized by red filled circles) and plant (lettuce, Lactuca sativa). FZB42 colonizes the root surface and is able to produce non-ribosomally cyclic lipopeptides, mainly surfactin and bacillomycin D and to a minor extent fengycin as indicated by the green circles (Chowdhury et al., 2015). It is very likely, but not shown until now, that VOCs (e.g., acetoin, 2,3-butandiol), and small peptides (e.g., plantazolicin, amylocyclicin) are also produced in vicinity of plant roots. Direct antibiosis and competition for nutrients (e.g., iron) suppresses growth of bacterial and fungal plant pathogens in the rhizosphere. However, these effects seem to be of minor importance, since the composition of the root microbiome is not markedly affected by inoculation with FZB42 (Erlacher et al., 2014), and the number of vegetative B. amyloliquefaciens cells on root surfaces is steadily decreasing (Kröber et al., 2014). Due to production of Bacillus signaling molecules (cLPs and VOCs) and in simultaneous presence of R. solani, the plant defensing factor 1.2 (PDF1.2) as indicated by the green-filled red circles is dramatically enhanced and mediates defense response against plant pathogens (Chowdhury et al., 2015). The picture of the lettuce plant (Lactuca crispa) was taken from Bock, 1552, p. 258).
Future work will focus on further elucidating the effects exerted by secondary metabolites produced by plant-growth-promoting Bacilli within plant rhizosphere on plant health and growth. The response of the plant in simultaneous presence of the beneficial Bacillus and the pathogen will be of special interest. In this context, use of a model bacterium such as FZB42 seems to be advantageous and should make results more comparable.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
Many of the results mentioned in this review have been obtained in frame of the collaborative projects ‘PATHCONTROL’ and the Chinese–German cooperation program. Both projects were financially supported by the German Ministry for Education and Research, BMBF. RB wish to thank Joachim Vater, Technical University Berlin, for long-lasting trustful collaboration in elucidating Bacillus secondary metabolites.
References
Arguelles Arias, A., Ongena, M., Devreese, B., Terrak, M., Joris, B., and Fickers, P. (2013). Characterization of amylolysin, a novel lantibiotic from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens GA1. PLoS ONE 8:e83037. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083037
Aziz, R. K., Bartels, D., Best, A. A., DeJongh, M., Disz, T., Edwards, R. A., et al. (2008). The Rast server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genomics 9:75. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-75
Bock, H. (1552). De Stirpium, Earum, Quae in Germania Nostra Nascuntur Commentariorum Libri Tres. Strassburg: Wendelin Rihel (first Latin edition).
Borriss, R. (2011). “Use of plant-associated Bacillus strains as biofertilizers and biocontrol agents,” in Bacteria in Agrobiology: Plant Growth Responses, ed. D. K. Maheshwari (Heidelberg: Springer), 41–76. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-20332-9_3
Borriss, R. (2013). “Comparative analysis of the complete genome sequence of the plant growth-promoting bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42,” in Molecular Microbial Ecology of the Rhizosphere, ed. F. J. de Bruijn (Hoboken, NJ: Wiley Blackwell Hoboken), 883–898.
Borriss, R. (2015). “Bacillus, a plant beneficial bacterium,” in Principles of Plant-Microbe Interactions. Microbes for Sustainable Agriculture, ed. B. Lugtenberg (Berlin: Springer), 379–391.
Borriss, R., Chen, X. H., Rueckert, C., Blom, J., Becker, A., Baumgarth, B., et al. (2011). Relationship of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens clades associated with strains DSM 7T and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum subsp. nov. based on their discriminating complete genome sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 61, 1786–1801. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.023267-0
Bulgarelli, D., Rott, M., Schlaeppi, K., Ver Loren van Themaat, E., Ahmadinejad, N., Assenza, F., et al. (2012). Revealing structure and assembly cues for Arabidopsis root inhabiting bacterial microbiota. Nature 488, 91–95. doi: 10.1038/nature11336
Burkett-Cadena, M., Kokalis-Burelle, N., Lawrence, K. S., van Santen, E., and Kloepper, J. W. (2008). Suppressiveness of root-knot nematodes mediated by rhizobacteria. Biol. Control 47, 55–59. doi: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2008.07.008
Cawoy, H., Debois, D., Franzil, L., De Pauw, E., Thonart, P., and Ongena, M. (2015). Lipopeptides as main ingredients for inhibition of fungal phytopathogens by Bacillus subtilis/amyloliquefaciens. Microb. Biotechnol. 8, 281–295. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.12238
Cawoy, H., Mariutto, M., Guillaume, H., Fisher, C., Vasilyeva, N., Thonart, P., et al. (2014). Plant defense stimulation by natural isolates of Bacillus depends on efficient surfactin production. MPMI 27, 87–100. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-09-13-0262-R
Chatterjee, S., Chatterjee, D. K., Lad, S. J., Phansalkar, M. S., Rupp, R. H., Ganguli, B. N., et al. (1992). Mersacidin, a new antibiotic from Bacillus: fermentation, isolation, purification and chemical characterization. J. Antibiot. 45, 832–838. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.45.832
Chen, X. H., Koumoutsi, A., Scholz, R., Eisenreich, A., Schneider, K., Heinemeyer, I., et al. (2007). Comparative analysis of the complete genome sequence of the plant growth-promoting bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. Nat. Biotechnol. 25, 1007–1014. doi: 10.1038/nbt1325
Chen, X. H., Koumoutsi, A., Scholz, R., Schneider, K., Vater, J., Süssmuth, R. D., et al. (2009a). Genome analysis of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 reveals its potential for biocontrol of plant pathogens. J. Biotechnol. 140, 27–37. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2008.10.011
Chen, X. H., Scholz, R., Borriss, M., Junge, H., Mögel, G., Kunz, S., et al. (2009b). Difficidin and bacilysin produced by plant-associated Bacillus amyloliquefaciens are efficient in controlling fire blight disease. J. Biotechnol. 140, 38–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2008.10.015
Chen, X. H., Koumoutsi, A., Scholz, R., and Borriss, R. (2009c). More than anticipated - production of antibiotics and other secondary metabolites by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 16, 14–24. doi: 10.1159/000142891
Chen, X. H., Vater, J., Piel, J., Franke, P., Scholz, R., Schneider, K., et al. (2006). Structural and functional characterization of three polyketide synthase gene clusters in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB 42. J. Bacteriol. 188, 4024–4036. doi: 10.1128/JB.00052-06
Chowdhury, S. P., Dietel, K., Rändler, M., Schmid, M., Junge, H., Borriss, R., et al. (2013). Effects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 on lettuce growth and health under pathogen pressure and its impact on the rhizosphere bacterial community. PLoS ONE 8:e68818. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068818
Chowdhury, S. P., Uhl, J., Grosch, R., Alquéres, S., Pittroff, S., Dietel, K., et al. (2015). Cyclic lipopeptides of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 subsp. plantarum colonizing the lettuce rhizosphere enhance plant defence responses towards the bottom rot pathogen Rhizoctonia solani. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-03-15-0066-R [Epub ahead of print].
Correa, O. S., Montecchia, M. S., Berti, M. F., Ferrari, M. C. F., Pucheu, N. L., Kerber, N. L., et al. (2009). Bacillus amyloliquefaciens BNM122, a potential microbial biocontrol agent applied on soybean seeds, causes a minor impact on rhizosphere and soil microbial communities. Appl. Soil Ecol. 41, 185–194. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2008.10.007
Cruz Ramos, H., Hoffmann, T., Marino, M., Nedjari, H., Presecan-Siedel, E., Dreesen, O., et al. (2000). Fermentative metabolism of Bacillus subtilis: physiology and regulation of gene expression. J. Bacteriol. 182, 3072–3080. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.11.3072-3080.2000
Debois, D., Jourdan, E., Smargiasso, N., Thonart, P., de Pauw, E., and Ongena, M. (2014). Spatiotemporal monitoring of the antibiome secreted by Bacillus biofilms on plant roots using MALDI Mass Spectrometry imaging. Anal. Chem. 86, 4431–4438. doi: 10.1021/ac500290s
Doornbos, R. F., van Loon, L. C., and Bakker, P. A. (2012). Impact of root exudates and plant defense signaling on bacterial communities in the rhizosphere. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 32, 227–243. doi: 10.1007/s13593-011-0028-y
Erlacher, A., Cardinale, M., Grosch, R., Grube, M., and Berg, G. (2014). The impact of the pathogen Rhizoctonia solani and its beneficial counterpart Bacillus amyloliquefaciens on the indigenous lettuce microbiome. Front. Microbiol. 5:175. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00175
Fajardo, A., and Martinez, J. L. (2008). Antibiotics as signals that trigger specific bacterial responses. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 11, 161–167. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2008.02.006
Fan, B., Borriss, R., Bleiss, W., and Wu, X. (2012). Gram-positive rhizobacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 colonizes three types of plants in different patterns. J. Microbiol. 50, 38–44. doi: 10.1007/s12275-012-1439-4
Fan, B., Chen, X. H., Budiharjo, A., Vater, J., and Borriss, R. (2011). Efficient colonization of plant roots by the plant growth promoting bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42, engineered to express green fluorescent protein. J. Biotechnol. 151, 303–311. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2010.12.022
Grosch, R., Junge, H., Krebs, B., and Bochow, H. (1999). Use of Bacillus subtilis as biocontrol agent. III. Influence of Bacillus subtilis on fungal root diseases and on yield in soilless culture. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 106, 568–580.
Guel, A., Kidoglu, F., Tuzel, Y., and Tuzel, I. H. (2008). Effects of nutrition and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens on tomato (Solarium lycopersicum L.) growing in perlite. Span. Agric. J. Res. 6, 422–429. doi: 10.5424/sjar/2008063-335
Hartmann, A., Schmid, M., van Tuinen, D., and Berg, G. (2009). Plant-driven selection of microbes. Plant Soil 321, 235–257. doi: 10.1007/s11104-008-9814-y
He, P., Hao, K., Blom, J., Rückert, C., Vater, J., Mao, J., et al. (2012). Genome sequence of the plant growth promoting strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum B9601-Y2 and expression of mersacidin and other secondary metabolites. J. Biotechnol. 164, 281–291. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2012.12.014
Herzner, A. M., Dischinger, J., Szekat, C., Josten, M., Schmitz, S., Yakéléba, A., et al. (2011). Expression of the lantibiotic mersacidin in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. PLoS ONE 6:e22389. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022389
Hofemeister, J., Conrad, B., Adler, B., Hofemeister, B., Feesche, J., Kucheryava, N., et al. (2004). Genetic analysis of the biosynthesis of non-ribosomal peptide- and polyketide like antibiotics, iron uptake and biofilm formation by Bacillus subtilis A1/3. Mol. Genet. Genomics 272, 363–378. doi: 10.1007/s00438-004-1056-y
Idris, E. E. S., Iglesias, D. J., Talon, M., and Borriss, R. (2007). Tryptophan dependent production of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) affects level of plant growth promotion by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 20, 619–626. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-20-6-0619
Jourdan, E., Henry, G., Duby, F., Dommes, J., Barthélemy, J., P., Thonart, P., et al. (2009). Insights into the defense-related events occurring in plant cells following perception of surfactin-type lipopeptide from Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 22, 456–468. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-22-4-0456
Kalyon, B., Helaly, S. E., Scholz, R., Nachtigall, J., Vater, J., Borriss, R., et al. (2011). Plantazolicin A and B: structure of ribosomally synthesized thiazole/oxazole peptides from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. Org. Lett. 13, 2996–2999. doi: 10.1021/ol200809m
Kierul, K., Voigt, B., Albrecht, D., Chen, X. H., Carvalhais, L. C., and Borriss, R. (2015). Influence of root exudate on the extracellular proteome of the plant-growth-promoting bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. Microbiology 161, 131–147. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.083576-0
Kinsinger, R. F., Shirk, M. C., and Fall, R. (2003). Rapid surface motility in Bacillus subtilis is dependent on extracellular surfactin and potassium ion. J. Bacteriol. 185, 5627–5631. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.18.5627-5631.2003
Kloepper, J. W., Leong, J., Teintze, M., and Schroth, M. (1980). Enhancing plant growth by siderophores produces by plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Nature 286, 885–886. doi: 10.1038/286885a0
Kloepper, J. W., Ryu, C.-M., and Zhang, S. (2004). Induced systemic resistance and promotion of plant growth by Bacillus spp. Phytopathology 94, 1259–1266. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO.2004.94.11.1259
Koumoutsi, A., Chen, X. H., Henne, A., Liesegang, H., Hitzeroth, G., Franke, P., et al. (2004). Structural and functional characterization of gene clusters directing nonribosomal synthesis of bioactive cyclic lipopeptides in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain FZB42. J. Bacteriol. 186, 1084–1096. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.4.1084-1096.2004
Kröber, M., Wibberg, D., Grosch, R., Eikmeyer, F., Verwaaijen, B., Chowdhury, S. P., et al. (2014). Effect of the strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 on the microbial community in the rhizosphere of lettuce under field conditions analyzed by whole metagenome sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 5:252. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00252
Li, B., Li, Q., Xu, Z., Zhang, N., Shen, Q., and Zhang, R. (2014). Response of beneficial Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SQR9 to different soilborne fungal pathogens through the alteration of antifungal compounds production. Front. Microbiol. 5:636. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00636
Liu, Z., Budiharjo, A., Wang, P., Shi, H., Fang, J., Borriss, R., et al. (2013). The highly modified microcin peptide plantazolicin is associated with nematicidal activity of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 97, 10081–10090. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-5247-5
Lopez, D., Fischbach, M. A., Chu, F., Losick, R., and Kolter, R. (2009a). Structurally diverse natural products that cause leakage trigger multicellularity in Bacillus subtilis. Proc. Natl. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 280–285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810940106
Lopez, D., Vlamakis, H., Losick, R., and Kolter, R. (2009b). Cannibalism enhances biofilm development in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 74, 609–618. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06882.x
Molohon, K. J., Melby, J. O., Lee, J., Evans, B. S., Dunbar, K. L., Bumpus, S. B., et al. (2011). Structure determination and interception of biosynthetic intermediates for the plantazolicin class of highly discriminating antibiotics. ACS Chem. Biol. 6, 1307–1313. doi: 10.1021/cb200339d
Müller, S., Strack, S. N., Hoefer, B. C., Straight, P. D., Kearns, D. B., and Kirby, J. R. (2014). Bacillaene and sporulation protect Bacillus subtilis from predation by Myxococcus xanthus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 80, 5603–5610. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01621-14
Nihorimbere, V., Cawoy, H., Seyer, A., Brunelle, A., Thonart, P., and Ongena, M. (2012). Impact of rhizosphere factors on cyclic lipopeptide signature from the plant beneficial strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens S499. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 79, 176–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2011.01208.x
Ongena, M., Jourdan, E., Adam, A., Paquot, M., Brans, A., Joris, B., et al. (2007). Surfactin and fengycin lipopeptdes of Bacillus subtilis as elicitors of induced systemic resistance in plants. Environ. Microbiol. 9, 1084–1090. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2006.01202.x
Pieterse, C. M. J., Zamioudis, C., Berendsen, R. L., Weller, D. M., Van Wees, S. C., and Bakker, P. A. (2014). Induced systemic resistance by beneficial microbes. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 52, 347–375. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-082712-102340
Qiao, J.-Q., Wu, H.-J., Huo, R., Gao, X.-W., and Borriss, R. (2014). Stimulation and biocontrol by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum FZB42 engineered for improved action. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 1:12. doi: 10.1186/s40538-014-0012-2
Raaijmakers, J., De Bruin, I., Nybroe, O., and Ongena, M. (2010). Natural functions of cyclic lipopeptides from Bacillus and Pseudomonas: more than surfactants and antibiotics. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 34, 1037–1062. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00221.x
Rahman, A., Uddin, W., and Wenner, N. G. (2014). Induced systemic resistance responses in perennial ryegrass against Magnaporthe oryzae elicited by semi-purified surfactin lipopeptides and live cells of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Mol. Plant Pathol. 16, 546–558. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12209
Renna, M. C., Najimudin, N., Winik, L. R., and Zahler, S. A. (1993). Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis alsS, alsD, and alsR genes involved in post-exponential phase production of acetoin. J. Bacteriol. 175, 3863–3875.
Rudrappa, T., Biedrzycki, M. L., Kunjeti, S. G., Donofrio, N. M., Czymmek, K. J., Paré, P. W., et al. (2010). The rhizobacterial elicitor acetoin induces systemic resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Commun. Integr. Biol. 3, 130–138. doi: 10.4161/cib.3.2.10584
Rueckert, C., Blom, J., Chen, X. H., Reva, O., and Borriss, R. (2011). Genome sequence of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens type strain DSM7T reveals differences to plant-associated Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. J. Biotechnol. 155, 78–85. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2011.01.006
Ryu, C.-M., Farag, M. A., Hu, C.-H., Reddy, M. S., Wei, H.-X., Paré, P. W., et al. (2003). Bacterial volatiles promote growth in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 4927–4932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0730845100
Sarosh, B. R., Danielsson, J., and Meijer, J. (2009). Transcript profiling of oilseed rape (Brassica napus) primed for biocontrol differentiate genes involved in microbial interactions with beneficial Bacillus amyloliquefaciens from pathogenic Botrytis cinerea. Plant Mol. Biol. 70, 31–45. doi: 10.1007/s11103-009-9455-4
Schneider, K., Chen, X. H., Vater, J., Franke, P., Nicholson, G., Borriss, R., et al. (2007). Macrolactin is the polyketide biosynthesis product of the pks2 cluster of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. J. Nat. Prod. 70, 1417–1423. doi: 10.1021/np070070k
Scholz, R., Molohon, K. J., Nachtigall, J., Vater, J., Markley, A. L., Süssmuth, R. D., et al. (2011). Plantazolicin, a novel microcin B17/streptolysin S-like natural product from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. J. Bacteriol. 193, 215–224. doi: 10.1128/JB.00784-10
Scholz, R., Vater, J., Budiharjo, A., Wang, Z., He, Y., and Dietel, K. (2014). Amylocyclicin, a novel circular bacteriocin produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. J. Bacteriol. 196, 1842–1852. doi: 10.1128/JB.01474-14
Velivelli, S., De Vos, P., Kromann, P., Declerck, S., and Prestwich, B. D. (2014). Biological control agents: from field to market, problems and challenges. Trends Biotechnol. 32, 493–496. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2014.07.002
Walsh, C. T., O’Brien, R. V., and Khosla, C. (2013). Nonproteinogenic amino acid building blocks for nonribosomal peptide and hybrid polyketide scaffolds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52, 7098–7124. doi: 10.1002/anie.201208344
Wang, S., Wu, H., Qiao, J., Ma, L., Liu, J., Xia, Y., et al. (2009). Molecular mechanism of plant growth promotion and induced systemic resistance to tobacco mosaic virus by Bacillus spp. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 19, 1250–1258. doi: 10.4014/jmb.0901.008
Wu, L., Wu, H., Chen, L., Xie, S., Zang, H., Borriss, R., et al. (2014). Bacilysin from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 has specific bactericidal activity against harmful algal bloom species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 80, 7512–7520. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02605-14
Yao, A. V., Bochow, H., Karimov, S., Boturov, U., Sanginboy, S., and Sharipov, K. (2006). Effect of FZB24 Bacillus subtilis as a biofertilizer on cotton yields in field tests. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 39, 1–6. doi: 10.1080/03235400600655347
Keywords: Bacillus amyloliquefaciens plantarum, FZB42, induced systemic resistance (ISR), non-ribosomal synthesized lipopeptides (NRPS), non-ribosomal synthesized polyketides (PKS), volatiles, plant growth promoting bacteria (PGPR)
Citation: Chowdhury SP, Hartmann A, Gao X and Borriss R (2015) Biocontrol mechanism by root-associated Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 – a review. Front. Microbiol. 6:780. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00780
Received: 11 February 2015; Accepted: 15 July 2015;
Published: 28 July 2015.
Edited by:
Essaid Ait Barka, Reims University, FranceReviewed by:
Sheng Qin, Jiangsu Normal University, ChinaLisa Sanchez, University of Reims Champagne-Ardenne, France
Copyright © 2015 Chowdhury, Hartmann, Gao and Borriss. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rainer Borriss, Fachgebiet Phytomedizin, Institut für Agrar- und Gartenbauwissenschaften, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Lentzeallee 55–57, 14195 Berlin, Germany, rainer.borriss@rz.hu-berlin.de
 Soumitra Paul Chowdhury
Soumitra Paul Chowdhury Anton Hartmann
Anton Hartmann XueWen Gao2,3
XueWen Gao2,3 Rainer Borriss
Rainer Borriss